Welcome to Natural Hazard: Egypt
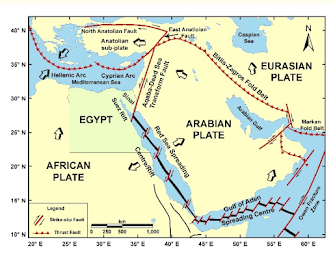
Egypt’s land frontiers border Libya to the west, Sudan to the south, and Palestine to the northeast. Egypt’s border with Sudan is notable for two areas, the Ḥalāʾib Triangle along the Red Sea and Biʾr Ṭawīl further inland, that are subject to differing claims by the two countries. In the north, its Mediterranean coastline is about 620 miles, and in the east, its coastline on the Red Sea and the Al Akaba Gulf is about 1,200 miles.
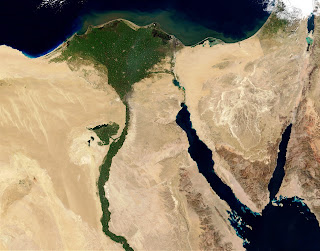
The topography of Egypt is dominated by the Nile. For about 750 miles (1,200 km) of its northward course throughout the Country, the river cuts its way through the bare desert, its narrow valley a sharply delineated strip of green, abundantly fecund in contrast to the desolation that surrounds it. From Lake Nasser, the river’s entrance into southern Egypt, to Cairo in the north, the Nile is hemmed into its trenchlike valley by bordering cliffs, but at Cairo, these disappear, and the river begins to fan out into its delta. The Nile and the delta form the first of four physiographic regions, the others being the Western Desert (Arabic Al-Ṣaḥrāʾ al-Gharbiyyah), the Eastern Desert (Al-Ṣaḥrāʾ al-Sharqiyyah), and the Sinai Peninsula.
References:
Encyclopædia Britannica, inc. (n.d.).Egypt. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved August 22, 2022, from https://www.britannica.com/place/Egypt

This is an amazing first post!- Looking forward to learning about Egypt's natural hazards with you.
ReplyDelete